Search Google or Type a URL: What It Means & How to Use It
Whenever you open up your web browser, you are tapped by an old-schooled message at the very top of your address bar: search google or type a URL. This is a very simple phrase which has become a part of our everyday experience of using the internet, and most of the people have not realized how powerful opportunities this phrase can offer. Be you a veteran internet user or a newcomer to internet browsing in the year 2026, when to use Google to search or simply type in an address can make or break your internet browsing performance.
This beginners guide towards this all-important browser feature will guide you through all you should know about this feature, making you turn into a master of the web practically. Starting with knowing the basic concept of a URL and culminating in the learning of the tricks and tricks of effective searching, we are going to play with the low-and-high-level aspects of the concept that the address bar of your browser is involved in.
What Does “Search Google or Type a URL” Mean?
Definition of the Term in Browser Context | Omnibox in Chrome, Edge, etc.
The term, search google or type a URL, is used in relation to the Two ways address bar in a web browser, the address bar of the latest versions of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox and Safari. It is a smart bar that frequently appears in Chrome as the so-called Omnibox, and it contains two functions at the same place in easy reach. As long as you see this prompt, what your browser is in effect giving you is two access ways to the internet situation that is your wanted destination.
You may either enter an entire address (URL) of a particular web site to access it directly, or you may enter keywords to search by Google or by your favorite search engine. This single platform has removed the use of different search boxes and address fields, making the process of browsing the web easier and simpler and simpler to navigate through the web by any person regardless of their level of expertise.
Why Browsers Show This Suggestion Before Typing
- User instructions: Gives novice users an idea that they can find their way in more than one way.
- Clarity of functionality: Makes it understandable that the bar has two purposes and not one.
- Less confusion: Regulates the ability of users to be confused where to type their searches or URLs.
- The promotion of exploration: The users should encourage trial and error, what works best regarding their needs.
- Personalization: Designs to attain learner-wide consistency.
- Time-saving prompt: Nudges a user to the most efficient way of using the specific need.
Understanding a URL (Web Address)
What a URL Is and Its Components
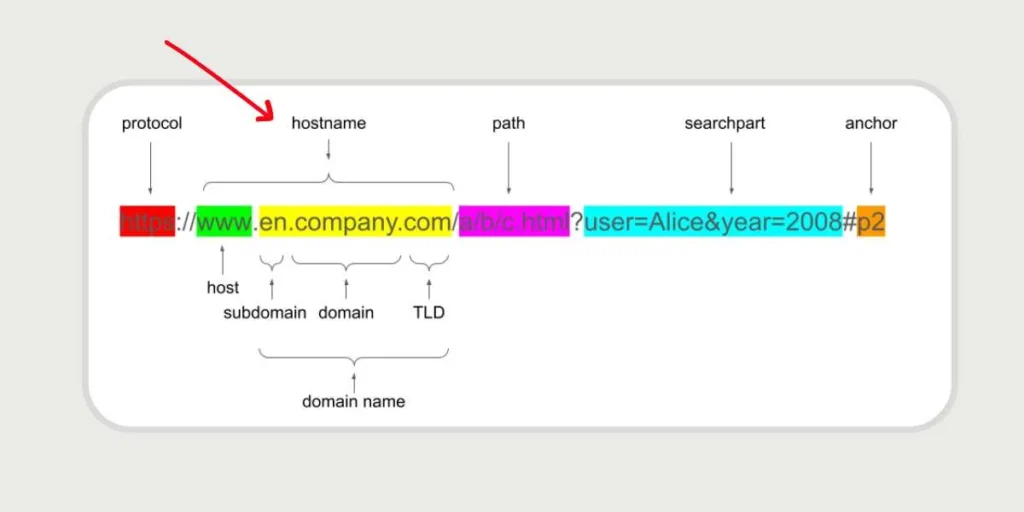
- Protocol: The prefix that is used to specify the manner in which data is transferred, i.e: prefix https or prefix http.
- Domain name: The primary name of the site (such as in the case of Google, weapons.com and so on).
- Subdomain: This is the prefix that will appear before the domain (such as the www or the mail) which is optional.
- Path: This is the subdivision within the domain (such as a subtopic such as /articles/guide)
- Parameters: Extra details sent to the site (with the beginning of the question mark)
- Fragment: Particular section in a page (dotted with a mark of the hashtag, the 3).
How URLs Work in Browsers and Servers
- DNS look up: Browser will create a translation of the domain name into an IP address.
- Server connection: Web browser links to the web server that the site is promoted in.
- Request sending: Browser makes a request to the server with regard to the particular page or resource.
- Data retrieval: This is the response of (Server) with the content of the requested webpage.
- Page rendering: Browser renders the content in a comprehensible document.
- Resource loading: Extra services such as scripts, videos, images and more are loaded.
Difference Between URLs and Search Terms
| Aspect | URL | Search Term |
| Format | Complete web address with domain | Keywords or phrases |
| Destination | Goes directly to a specific website | Shows search results page |
| Precision | Takes you to exact location | Provides multiple options |
| Speed | Fastest if you know the address | May require clicking through results |
| Examples | www.amazon.com, github.com/explore | “best laptops 2026”, “weather today” |
| Use of protocol | May include https:// | Never includes protocols |
How to Type and Access a URL | Step-by-Step Guide
- Open web browser: Open Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari or another browser that you choose.
- Click the address bar: Find and hit the bar at the top that is displayed as search Google or type a URL.
- Enter the full web address: The full web address has the domain extension (such as.com, .org, .net) typed in
- Insert protocol where necessary: There are browsers that demand the prefix “https://” to some web pages and as a result the prefix is automatically added.
- Spellcheck verification: Check the spelling to make sure that there is no mistake, even minor mistakes result in incorrect destination.
- Press Enter or Return: Press the key in order to visit the site.
- Waiting to load: Please wait till the page is loaded then it can be interacted with.
- Bookmarks often used sites: Bookmarks are the URLs of the sites that you visit regularly and need faster access during the future.
When to Use Search Instead of Typing URL
There are cases when searching for a site URL can be more reasonable than typing the site URL. Search method will be used when you are not sure about the exact spelling of the domain and want to see the official site before accessing the website, when you want to visit a very large site and are looking to access a particular page, when you know the direct page, and when you want to view related websites and alternatives. It can also come in handy when you know the brand of the product but do not know a specific domain name (.com, .org, .net, etc.).
Benefits
There are a number of benefits that come along with searching URLs using Google. You can see if there are several versions of the same site available, you can read casual descriptions and reviews of the search results and visit it, you can find official social media pages and the main one, and you can see the cache version in case of the offline of the original site, you can discover possible existence of phishing or fake websites, and you can get the autocomplete results and get the search results with more helpful information faster.
Google Indexing and How Search Results Are Displayed
- Crawling: Crawlers of Google search engines periodically scan and index about billions of Web pages.
- Ranking algorithm: page ranking is done in terms of relevance, quality and hundreds of other factors.
- Title display: The title tag in the page is seen as the blue link that can be clicked.
- Meta description: There is a short summary presented below the title that describes what is in the content.
- URL displayed: The real web address is seen in green and is seen below the title.
- Rich snippets: Rating, pictures, or structured information is also likely to happen.
- Placement: Ads are placed at the top and are marked with Ad.
- Snippets: Common snippets can be defined as special boxes positioned above ordinary results.
Search vs Type URL: Pros and Cons
| Method | Pros | Cons | Best Use Case |
| Typing URL | Fastest direct access; No intermediary pages; More private (no search record); Exact destination guaranteed; Works offline for cached pages | Requires exact address knowledge; Typos lead to errors; No discovery of alternatives; Must remember full domain | When you know the exact website address; For frequently visited sites; When privacy is a priority; For accessing bookmarked resources |
| Searching Google | Don’t need exact URL; Find related sites; Verify legitimacy first; Discover new resources; Get descriptions before clicking | Takes extra steps; Creates search history; May show ads first; Slower than direct access; Requires internet connection | When unsure of exact address; For discovering new websites; When comparing options; For finding specific pages within large sites |
Mobile and App Considerations
- Touch-friendly interface: Mobile browsers modify the “searchgoogle or typeaurl” field to have more pronounced touches.
- Voice input support: The majority of mobile browsers have voice search in the address bar.
- Autocomplete significance: By having fewer keys, predictive text is more important on mobile computing devices.
- App deep linking: On certain searches specific apps may be displayed in place of websites.
- Web awareness: The use of a direct URL can consume less data than loading of search results initially.
- Browser shortcuts: Mobile browsers can have shortcuts of commonly visited websites displayed as icons beneath the address bar.
- Copy and paste option: A long URL is simpler to paste as opposed to typing on a mobile phone.
- Combination of QR codes: Most mobile browsers are capable of scanning QR codes and opening URLs.
- Incognito mode: Private browsing is identically applicable when you are searching on Google or when typing the address in the search engine.
- Cross-due device sync: Syncing access can be easily accessed across devices with bookmarks as well as history being banked.
Conclusion
When to search via a search engine, for example Google or typing a URL, just knowing when to do that is a basic skill that improves the efficiency of browsing the web and the experience of using the internet in general. Even in 2026, the dual-functionality system will remain the main entry point to the web and it is important to master both methods. Regardless of how fast and accurate and precise typing in URLs is, or how much time it takes to find and confirm anything through a Google search, both of these options have a place in your digital toolkit.
The trick is that in one case or another it is the recognition which requires what method to use, whether by direct URL entry to websites that you already know and trust or exploration through searching. The mere message to type into the search box or open a web address, as the browsers constantly upgrade and gain smarter predictions and increased security options, will always stay with you and help guide you through the endless digital space. With the information acquired in this guide, you will waste less time, be more secure on the internet, and will make better decisions each time you open the address bar to your browser.
Explore Our Blogs for More Content Like This: MangoRank
FAQs
Do you think it is safer to type in a URL or to search it?
Direct typing of a URL is normally more secure if what you need is the exact address of a site since you will not face the chances of clicking on unhealthy search results or advertisements. Nevertheless, it is always good to search initially so as to ensure that you are on the right official site.
Why does the browser sometimes search Louis?
Up to now I typed the URL but it does not direct me to my URL? Otherwise, (without the domain extension (.com, .org, etc.)) or when you have a typo, your browser sees whatever you type in as a search query and not a URL. There should be a full domain in direct navigation.
Is it possible to alter the search engine used when searching using the address bar?
Yes, it is possible to make any major browser switch the default search engine. Bing, DuckDuckGo, and other search engines are open to the switching option, depending on your choice as compared to Google.
Does a site address require typing of a prefix (2 letters) namely www?
In the vast majority of situations no. The current browsers add the prefix “www” automatically as required. What the matter is is that you can easily get to the site by typing the name of the company with the word “google” followed by dot com, which will allow you to get to the site of W W Well, Google.com.
What do I do when typing the wrong URL and learning that there is an error in it?
To start with, look out for typos in the address. Make sure you do not leave out the right domain extension in this. In case of the problem persisting, instead, use the name of the web site, or use a service such as Down for Everyone or Just Me, to test if the web site is temporarily offline or not.


